NEGATIVE STOCK REPORT
A Negative Stock Report is a report used in inventory management and accounting to highlight instances where the stock of certain products or items in a warehouse or store is recorded as being negative. This means that the system shows more items as sold or issued than what was available in the inventory. Negative stock situations usually occur due to errors, discrepancies, or inconsistencies in stock management.
User Access
Who Can Access
- Pothys admin
- Head cashier
- Sales Manager
- manager
What User Can Do
- View Reports
- Analyze Sales
- Export
Pre-Requisite Activities
- Date range
- Cashier
Business Rules
1. Stock Level Threshold for Reporting Negative Stock
- Rule: Any product with a negative stock level (i.e., where the recorded quantity is less than zero) should trigger an entry in the Negative Stock Report.
2. Causes of Negative Stock
- Rule: Negative stock should be associated with specific causes that are recorded within the report or system.
3. Real-Time Inventory Updates
- Rule: Inventory levels must be updated in real-time to prevent situations where stock is issued or sold before it is physically available.
4. Automated Alerts for Negative Stock
- Rule: The system should automatically generate alerts whenever negative stock levels are detected.
5. Stock Adjustments and Manual Corrections
- Rule: If negative stock arises due to system errors or human mistakes, manual stock adjustments should be used only after careful verification. Adjustments must be documented and reviewed.
User Interface
Step 1 : Select ‘Negative Stock Report’ in Menu -> Sales reports > Manager report > Negative Stock Report or Search Negative Stock Report.
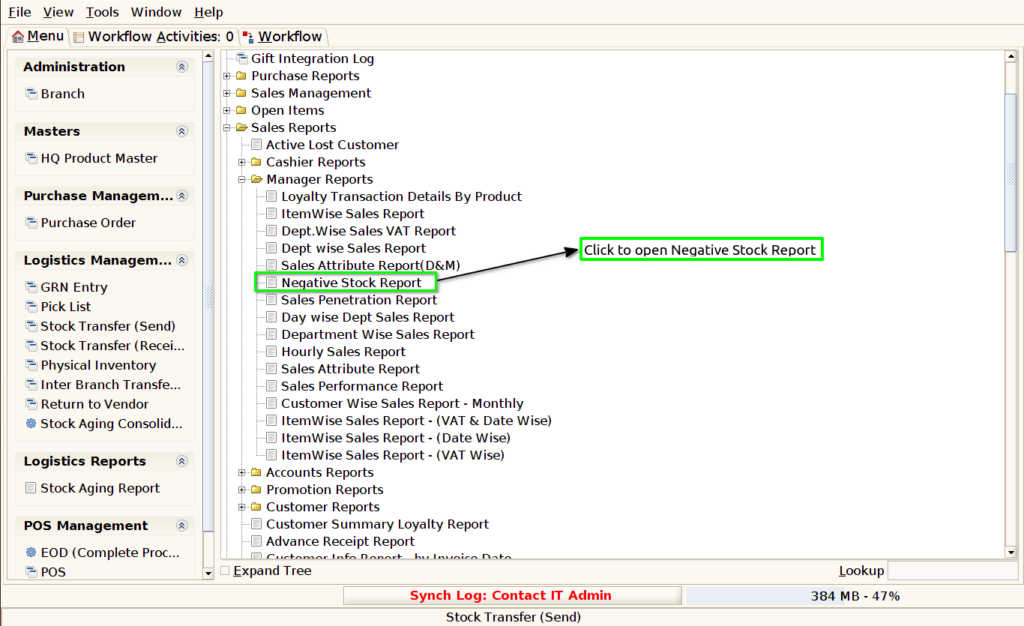
Step 2 : Select the date range and attribute to open the Negative Stock Report.
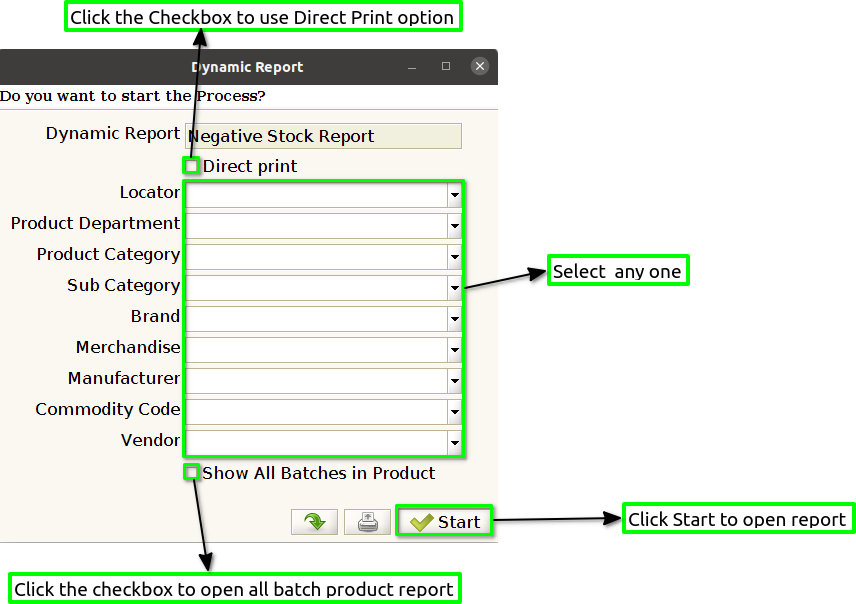
Step 3 : To view a preview of the Negative Stock Report in Jaldi.
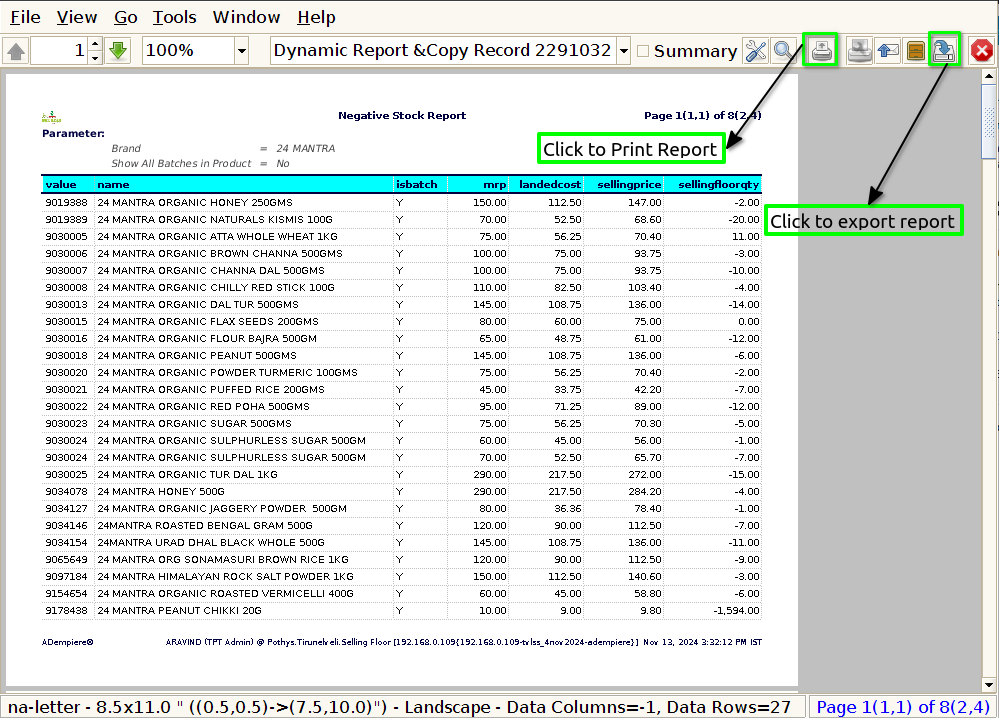
Value : A unique code (product code) used to identify each product in the inventory system. The product code is critical for tracking and managing inventory.
Name : The name of the product (e.g., Widget A, Widget B, Gadget X). Displaying the name allows for easier understanding of which items are affected by negative stock, especially for non-technical users.
Is Batch : Including an “Is Batch” field in a Negative Stock Report can be particularly useful for businesses that manage batch-tracked inventory. This field indicates whether the product in question is
batch-controlled or tracked by specific production or shipment batches.
MRP : This is the price at which the product can be sold to the end customer. It is typically higher than the Cost Price and Selling Price. Including the MRP in the Negative Stock Report provides visibility into the potential revenue loss if the product had been sold at the maximum retail price instead of the selling price.
Landed Cost : Including Landed Cost in a Negative Stock Report is important because it reflects the total cost of a product after accounting for not just the purchase price but also any additional costs involved in bringing the product into inventory.
Selling Price : Including the Selling Price in the Negative Stock Report is important because it helps businesses understand the revenue impact of negative stock situations. The Selling Price is the price at which the product is typically sold to customers, and tracking it against negative stock can help quantify the potential lost revenue or missed sales opportunities.
Selling Floor Quantity : This column represents the amount of product physically available on the sales floor. This can be critical in identifying whether a product is “out of stock” in the back-end system but still available for sale on the floor.
In-transit Quantity : Tracking In-transit Quantity in a Negative Stock Report helps to identify the real-time availability of stock, especially in cases where negative stock is recorded due to pending shipments.
Godown Quantity : If stock is available in a godown but negative stock is reported at the sales floor or retail location, it helps prevent mismanagement of inventory across locations.
On hand Quantity : The On-hand Quantity gives you the actual, real-time inventory available at any given location. It can be particularly useful when reconciling or investigating negative stock scenarios, where the system shows stock shortages.
Stock value by Land Cost : The Shock Value by Landed Cost in the Negative Stock Report is a crucial metric for assessing the financial exposure caused by negative stock situations.
Stock value by MRP : The Shock Value by MRP (Maximum Retail Price) in a Negative Stock Report represents the potential revenue loss associated with negative stock situations, calculated based on the MRP of the product.
Stock value by Selling Price : The Shock Value by Selling Price in a Negative Stock Report calculates the potential lost revenue due to negative stock situations, based on the Selling Price of the product.
Brand : In the Negative Stock Report, including the Brand of each product is useful for understanding which brands are experiencing stock shortages. This information can help identify supply chain issues or product popularity by brand, allowing businesses to manage inventory and stock replenishment strategies more effectively.
Merchandise : Including Merchandise in the Negative Stock Report allows businesses to track stock levels specifically for merchandise items.
category : Including Category in the Negative Stock Report enables better tracking and analysis of product shortages by grouping products into logical categories.
Department : This column specifies the department to which the product belongs. Examples of departments could include Electronics, Clothing, Furniture, Grocery, Pharmacy, or any other category used in your inventory system.
Vendor : This column identifies the vendor or supplier who provided the product. Vendors are typically tracked in your purchase order system, and their information can be linked to specific products through product catalogs or supplier databases.
Last Inventory : This column represents the inventory quantity at the time of the last stock count (e.g., from the previous inventory check or snapshot). This helps compare historical stock levels with current levels and provides insights into why negative stock occurred.
Adjustment Quantity : Adjustments often occur when discrepancies arise between recorded stock levels and the actual quantities on hand, or when inventory errors are detected (such as stock damage, theft, or data entry mistakes).
Movement Date : This column represents the date when a stock movement (sale, receipt, adjustment, transfer) occurred. By showing the Movement Date, businesses can identify the specific time frame during which the negative stock situation occurred and whether it is associated with any particular events (e.g., large sales, stock adjustments, etc.).