TO CREATE A E-INVOICE REPORT FOR GST
An e-invoice report for GST (Goods and Services Tax) refers to a digital invoice system implemented by the Government of India to streamline the invoicing process for businesses. This initiative is part of the broader Goods and Services Tax system aimed at enhancing transparency, reducing tax evasion, and improving compliance.
User Access
Who Can Access
- Pothys admin
- Back Office
- Purchase Manager
- Manager
What User Can Do
- View Reports
- E-Invoice Report for GST
Pre-Requisite Activities
- Date Invoiced
- Bill no
Business Rules
- Compliance with GST Regulations-Ensure that the e-invoice format complies with the latest GST legislation and regulations relevant to your jurisdiction.
- Mandatory Fields -Supplier Information (GSTIN, Name, Address)
- Validation of GSTIN-Implement a validation mechanism for GSTIN to ensure it complies with the format and is registered in the GST system before generating an e-invoice.
- Unique Invoice Number Generation-Ensure that each e-invoice has a unique invoice number to prevent duplication and maintain accurate records for audit purposes.
- Digital Signature and Authentication-Utilize digital signatures for e-invoices to ensure authenticity and integrity of the data being transmitted.
- Real-time Reporting-Configure the system to report e-invoices to the GST portal in real-time to ensure timely filing and avoid penalties.
- Cancellation and Revisions-Establish rules for the cancellation and revision of e-invoices, including necessary documentation and timelines for reporting cancellations.
- Data Archiving and Retrieval-Preserve e-invoice data for a specified retention period (typically 6 or 8 years as per local laws) for audit and compliance purposes. This information must be easily retrievable.
- Handling of Credit Notes and Debit Notes-Set rules for generating e-invoices for credit notes and debit notes, ensuring they reference the original invoice and comply with GST rules.
- Invoice Format-Support multiple formats for e-invoices (e.g., JSON, XML) as per the requirements set by the GST portal.
User Interface
STEP 1: To select a E-invoice Report for GST.
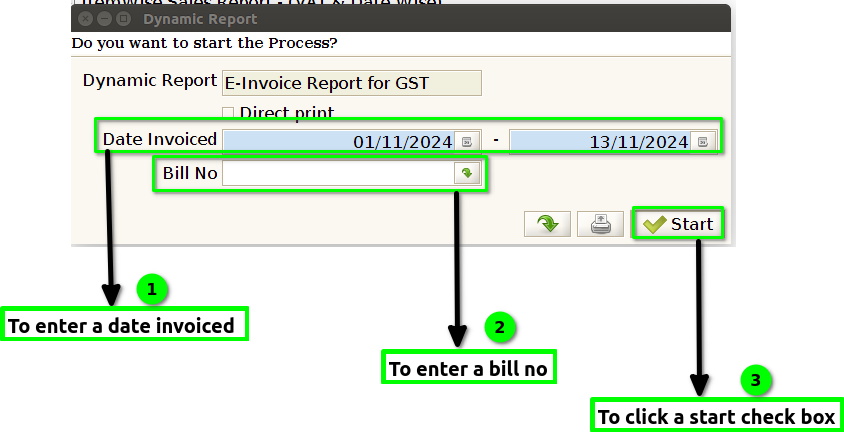
STEP 2: To enter a Date Invoiced and to enter a Bill no.To click a start check box then to run the process.
STEP 3: Once to complete the process to show the report based on the given data.
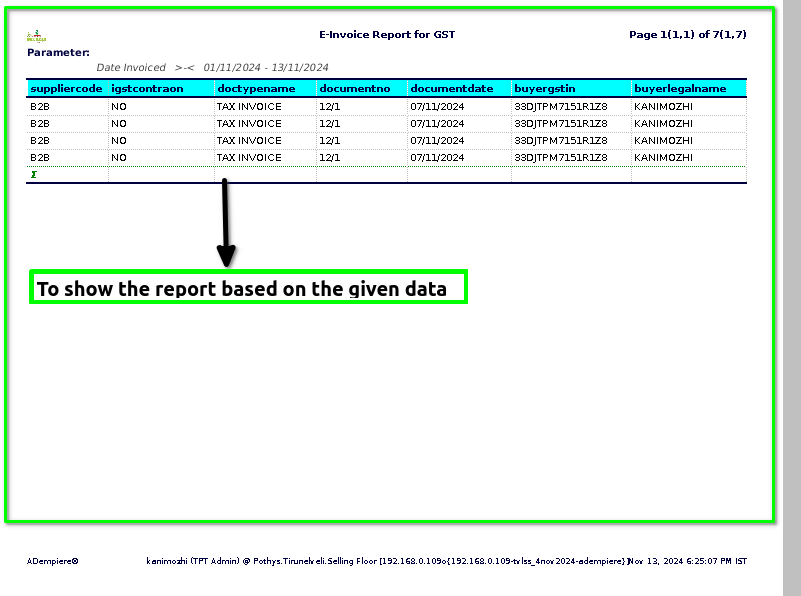
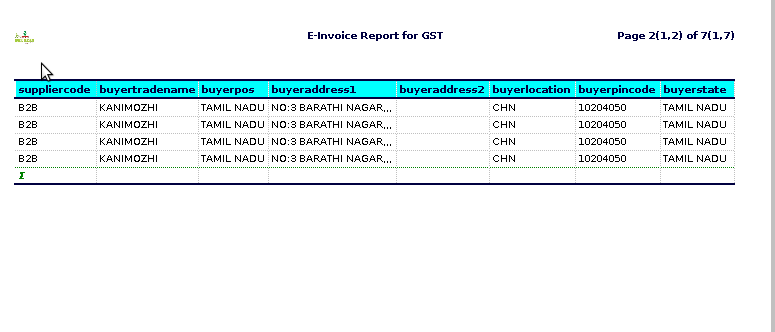
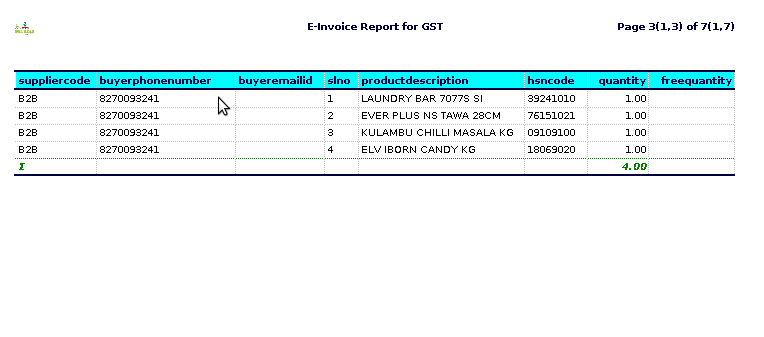

STEP 4: Supplier code– is a unique identifier assigned to a supplier or vendor by a company or organization. It is often used in procurement and supply chain management to streamline processes such as purchasing, invoicing, and inventory management.
IGST Contraon-IGST stands for Integrated Goods and Services Tax. It is a type of indirect tax in India that is applied to the supply of goods and services when they are transported across state borders.
Document type name- typically refers to the classification or categorization of the document that contains the sales transaction details.
Document number-typically refers to a unique identifier assigned to each transaction or sale. This number is used for record-keeping and tracking purposes, helping businesses and financial institutions.
Document date – typically refers to the date on which the transaction was recorded or processed.
Buyer GSTIN– (Goods and Services Tax Identification Number) in a credit card sales report refers to the unique identification number assigned to a buyer (individual or business) who is registered under the Goods and Services Tax system in India.
Buyer legal name -typically refers to the name of the individual or business entity that appears on the credit card used for the transaction.
Buyer POS -generally refers to the point of sale (POS) transaction where a buyer uses a credit card to make a purchase.
Buyer address 1& 2- refers to the physical address of the customer who made the purchase.
Buyer location– refers to the geographical location where a credit card transaction was made.City and State, Country,Store Location.
Buyer pincode– (more commonly referred to as “buyer postal code” or “buyer ZIP code” in some regions) typically represents the postal code of the buyer’s billing address.
Buyer phone number– typically refers to the contact number of the customer who made the purchase using their credit card.
Buyer state-typically refers to the geographic location of the buyer or customer who made the purchase using the credit card.
Buyer mail ID– typically refers to the email address of the customer or buyer who made the purchase using their credit card.
Serial number-(often referred to as a transaction or reference number) typically serves as a unique identifier for each transaction. This number helps in tracking and managing sales.
Product description– refers to a detailed account of the specific credit card products that are being offered.
HSN (Harmonized System of Nomenclature) code -is a standardized numerical method of classifying goods that is internationally recognized. In the context of credit card sales reports, particularly in countries like India, the HSN code is used for identifying the nature of the goods or services sold.
Quantity-typically refers to the number of individual items or transactions that have been processed using credit cards.
Free quantity– typically refers to the number of items or units sold that are given away for free as part of a promotion or marketing strategy.
Unit– typically represents the individual items or products sold. For example, if a retailer sells 100 pairs of shoes, the unit would be “shoes,” and the total number sold would be 100 units.
Unit Price– refers to the price of each individual unit. In the previous example, if each pair of shoes is sold for $50, the unit price would be $50.
Gross amount– refers to the total revenue generated from credit card transactions before any deductions are made.
Discount– refers to a reduction in the selling price of goods or services applied to the transactions processed through credit card payments.
pretax value– in a credit card sales report refers to the total amount of sales transactions before any taxes have been applied.
Taxable value– typically refers to the portion of the sale amount that is subject to sales tax.
Goods and Services Tax (GST) rate-applied to credit card sales can vary depending on the nature of the goods or services being sold and the regulations in place in each country or region.
SGST1 -stands for State Goods and Services Tax. It is part of the Indian taxation system and applies to the sale of goods and services within a state.
CGST -stands for Central Goods and Services Tax. In the context of a credit card sales report, CGST amount refers to the portion of the Goods and Services Tax (GST) that is levied by the central government on goods and services sold.
IGST -refers to Integrated Goods and Services Tax. IGST is applicable on inter-state supply of goods and services and is a part of the Goods and Services Tax (GST) structure.
Cess Rate– In some jurisdictions, cess is an additional charge on certain products or services, often intended to fund specific initiatives (e.g., education, health, etc.).
Cess amtdval -can imply a type of tax imposed over and above the basic tax (like GST in India). The “cess amount” is the specific amount that is added to the base transaction value,AD value in this context might stand for “Added Value” or “Amount Due,” although the exact meaning.
Cess nonadv val amt- typically refers to the “cess” (a type of tax) applied to non-advancing transactions or sales that do not have an advancing or promotional value.
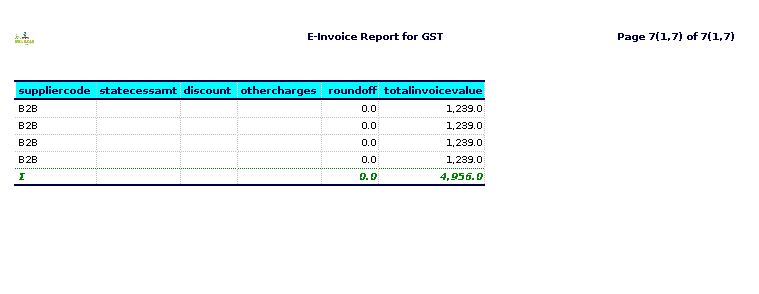
State cess rate-refer to taxes or levies imposed by a state government on certain transactions.
Total invoice value- typically refers to the cumulative sum of all sales transactions made using credit cards over a specific period.
Total taxable value – typically refers to the total sum of sales transactions that are subject to sales tax.
Item Total -typically refers to the total sum of the individual item prices that have been sold during a specific period.
Other charges-can refer to various fees or costs associated with credit card transactions that are not directly linked to the sale itself.
Roundoff– typically refers to the process of adjusting sales figures to the nearest whole number, often to make accounting simpler or to conform to certain financial reporting standards.
Training Videos
FAQ
SOP